Types System
CityScope (CS) Types are the basic land-use units that can be combined and arranged to represent urban environments within the CityScope platform. CS Types are assigned to each cell within the grid that is overlaid over the urban area of enquiry. The grid provides unified segmentation, scale and a level of abstraction that can be easily manipulated by users. Each cell within the grid can either be fixed or dynamic, depending on project limits; fixed cells within a grid are not intended to be changeable by users; dynamic cells are intended for manipulation to interact with the CityScope platform. Interactions take place as users manipulate Types within the project area.
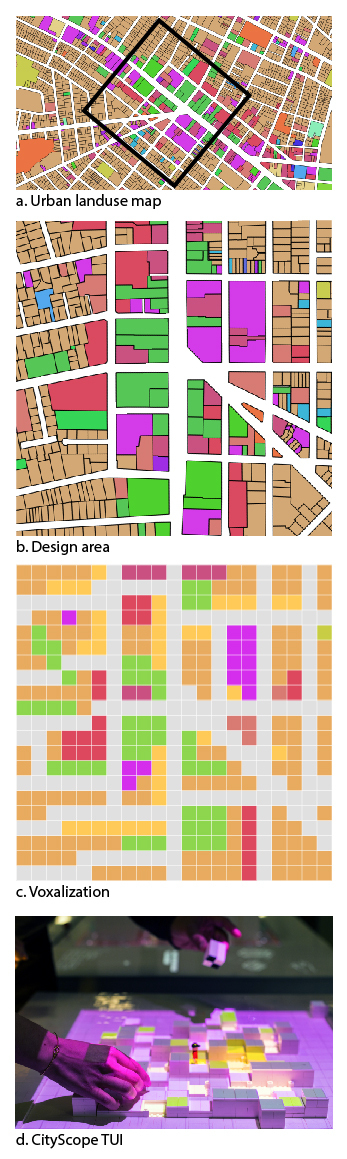
CS Types are represented by tiles that are set within the cells of a grid. At minimum, each tile must include land use and economic activity data, which can be complemented with additional dimensions of information that are assigned by users during the commissioning of a table. Additional information that can be assigned to a CS Type includes, but is not limited to, the acoustic characteristics, demographic information, and/or the utilization of a type.
To standardize the analysis and visualization modules, the CityScope platform uses unified data classifications to define each Type. CS Types may differ from project to project depending on the programming and intervention under investigation. To standardize how CS Types are defined, the classification uses unified dictionary of attributes that include, but are not limited to, land-use and economic activity, as defined by the American Planning Association, Land-Based Classification Standards or LBCS, and the North American Industry Classification System or NAICS, for the associated economic activity. Additional characteristics can be added when project specific modules are being used.
LBCS - Land Use Classification Notation:
The LBCS classification system extends the notion of land uses by refining traditional categories into multiple dimensions, including activity, function, building type, site development character, and ownership constraints. Each dimension has its own set of categories and subcategories for classifying land uses. By classifying every land-use across multiple dimensions, users can have precise control of land-use classifications. Codes are generated using a numerical classification outlined in the LBCS manual:
https://planning-org-uploaded-media.s3.amazonaws.com/document/LBCS.pdf
Schema Description:
- X 0 0 0 - First level classification - General
- XX 0 0 - 2nd level - Type
- XXX 0 - 3rd level - Activity
- XXXX - 4th level - Specific Activity
Most CS Types may only include Activity dimensions, however additional LBCS information can be added.
NAICS - Economic Activity Classification Notation:
In addition to the LBCS classifications, the NAICS codes are a standard used by Federal statistical agencies in classifying business establishments for the purpose of collecting, analyzing, and publishing statistical data related to the U.S. business economy.Codes are generated using a numerical classification outlined in the NAICS manual:
https://www.census.gov/eos/www/naics/2017NAICS/2017_NAICS_Manual.pdf
chema Description:
- X 0 0 0 0 - First level classification - Industry Sector (20 broad sectors up from 10 SIC)
- XX 0 0 0 - 2nd level - Industry Sub sector
- XXX 0 0 - 3rd level - Industry Group
- XXXX 0 - 4th level - Industry
Sample CS Types:
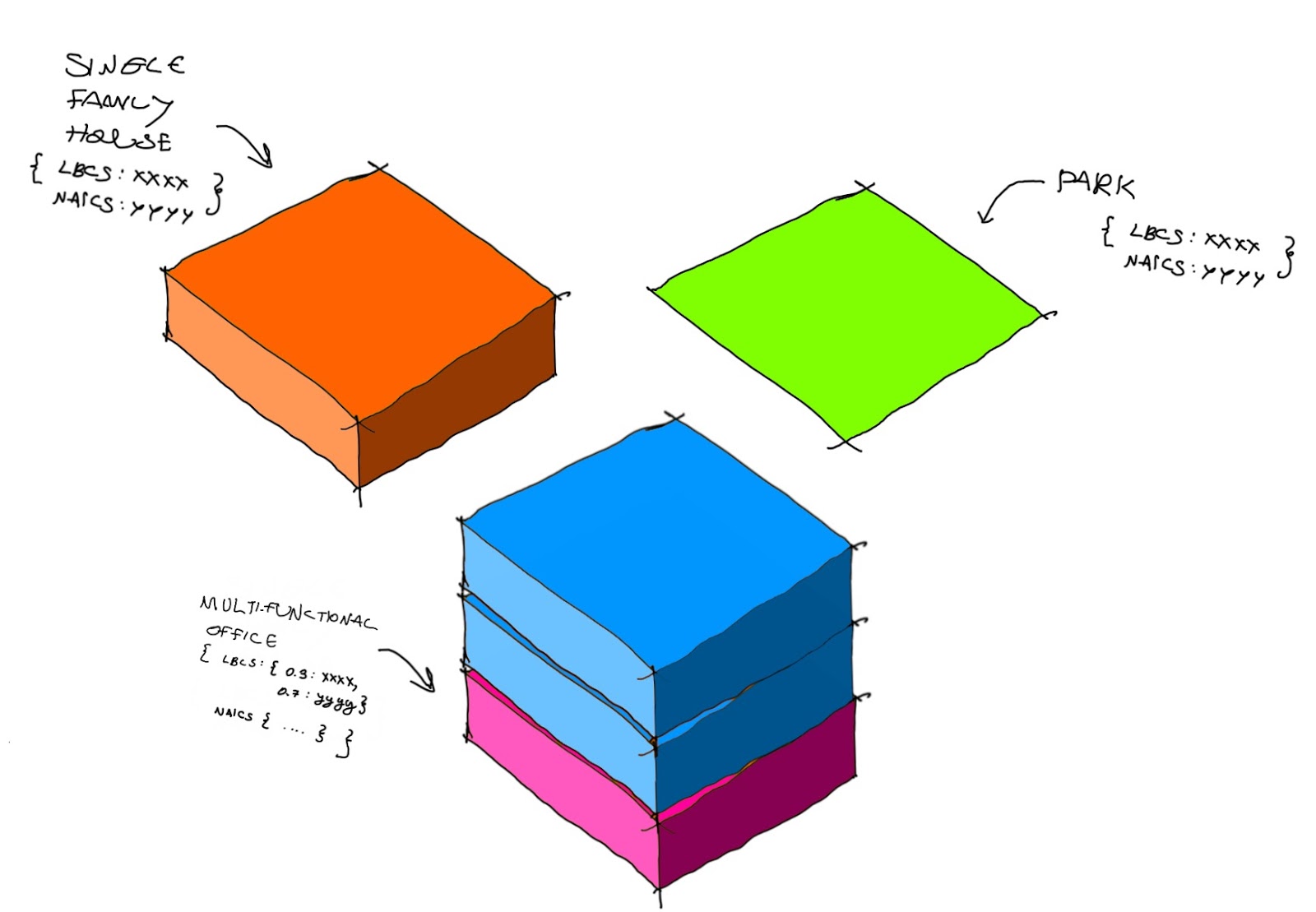
As an example exercise we will define 3 of the most popular CS types: A simple single use tile like a park, a single use tile of housing, and a multi use tail mixing office and shopping:
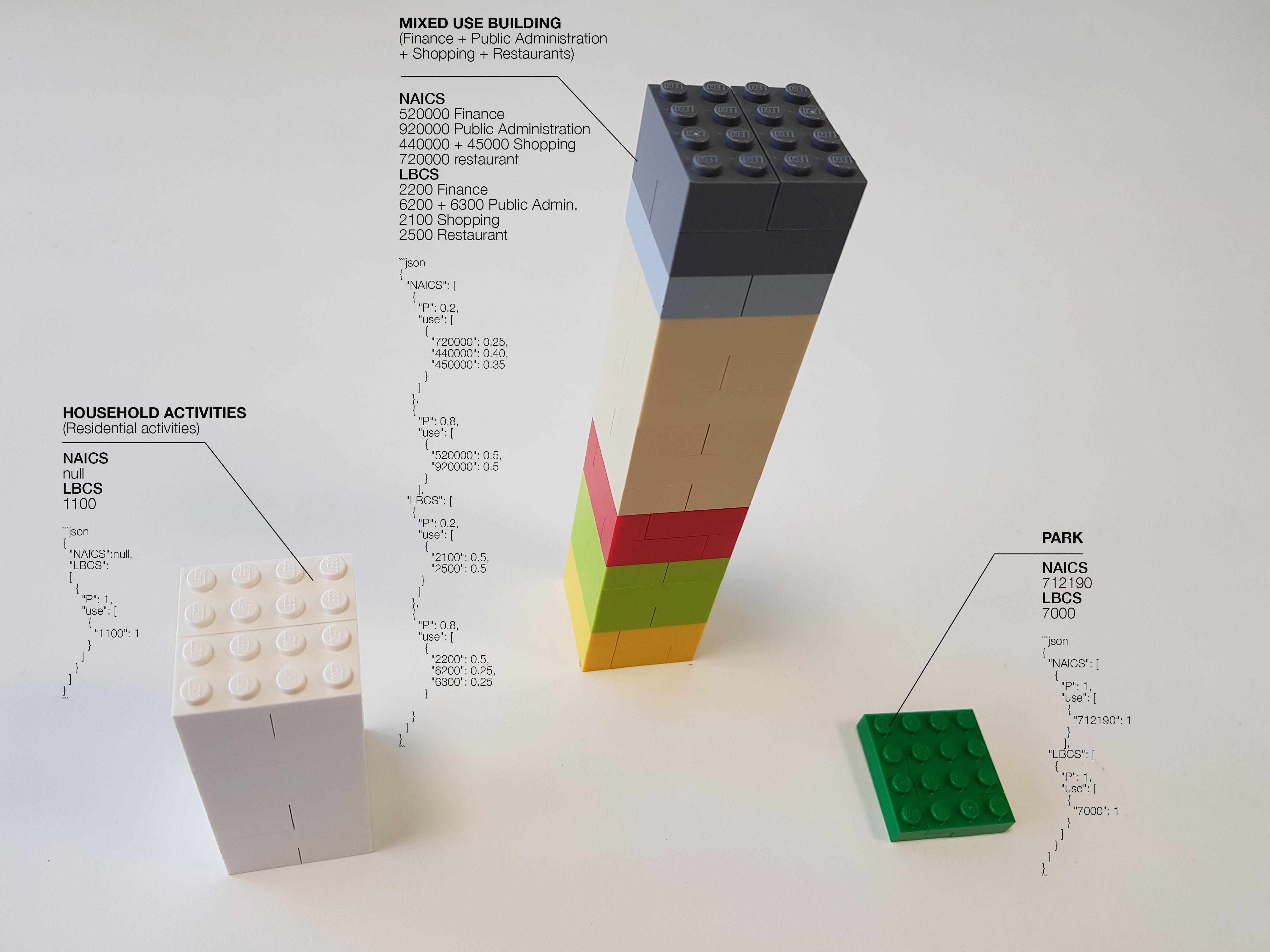
Park
No floors, 100% of park activity. NAICS mapping = 712190. LBCS mapping = 7000

{
"NAICS": [
{
"P": 1,
"use": [
{
"712190": 1
}
],
"LBCS": [
{
"P": 1,
"use": [
{
"7000": 1
}
]
}
]
}
Household activities (Residential activities)
Individual housing building, 100% of Residential activities. NAICS mapping = null (Since NAICS is the "standard used by Federal statistical agencies in classifying business establishments"; housing doesn't have a correlation in NAICS). LBCS mapping = 1100

{
"NAICS": null,
"LBCS": [
{
"P": 1,
"use": [
{
"1100": 1
}
]
}
]
}
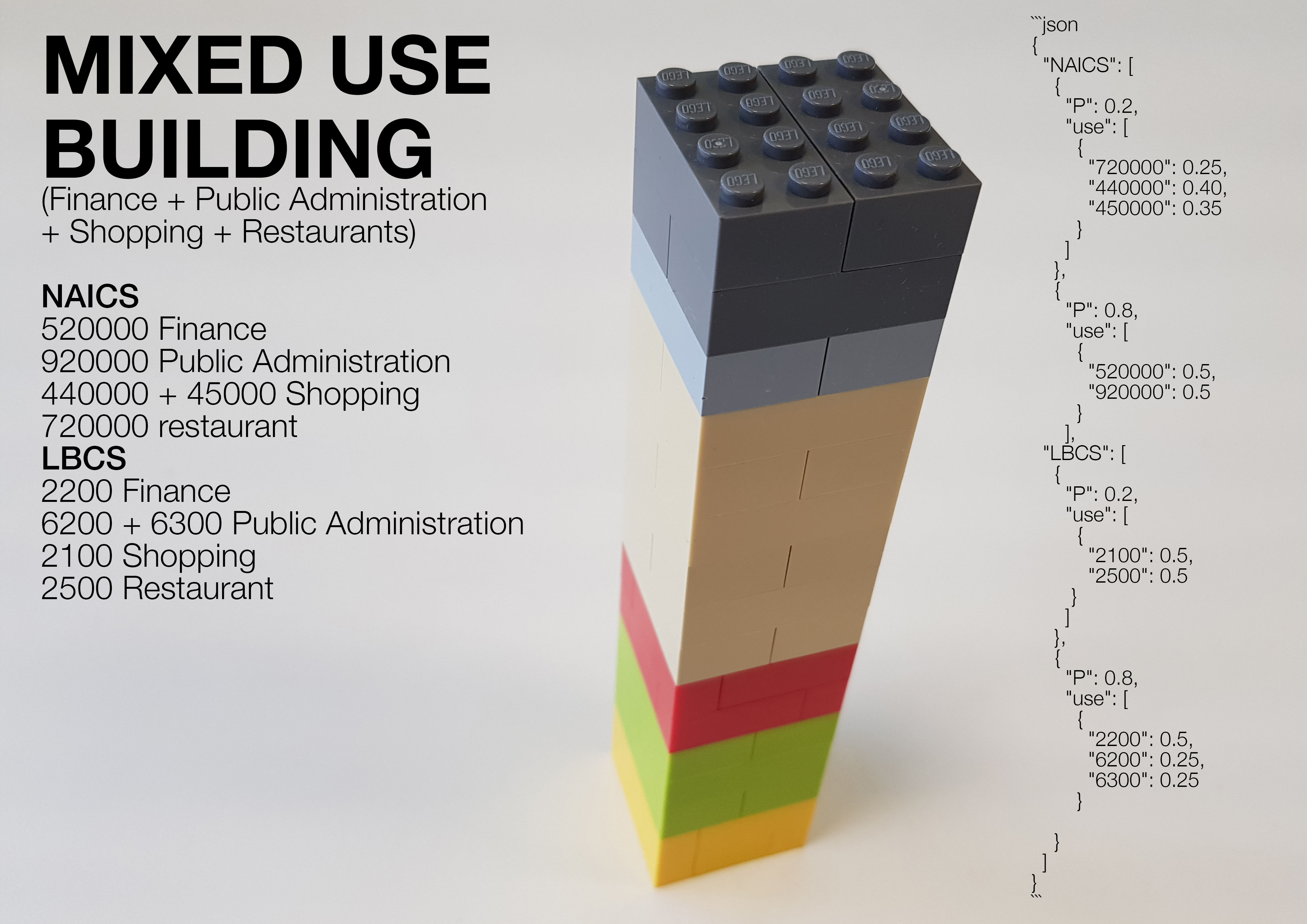
Mixed use Building (Finance + Public Administration + Shopping + Restaurants)
Office and Shopping building: 80% of Financial activities, 20% of Restaurant and shopping activities. NAICS mapping = 520000 finance, 920000 Public Administration, 440000 + 45000 shopping, and 720000 restaurant. LBCS mapping = 2200 finance, 6200 + 6300 Public Administration, 2100 shopping, and 2500 restaurant
- The lower 20% of floors are devoted to a mix of shopping 75% and restaurants 25%
- The upper 80% of floors and is devoted to a mix of finance 50% and Public Administration 50%
{
"NAICS": [
{
"P": 0.2,
"use": [
{
"720000": 0.25,
"440000": 0.40,
"450000": 0.35
}
]
},
{
"P": 0.8,
"use": [
{
"520000": 0.5,
"920000": 0.5
}
],
"LBCS": [
{
"P": 0.2,
"use": [
{
"2100": 0.5,
"2500": 0.5
}
]
},
{
"P": 0.8,
"use": [
{
"2200": 0.5,
"6200": 0.25,
"6300": 0.25
}
]
}
]
}
References
ANEX
LBCS and NAICS Crosspath
Mapping Correlation between LBCS and NAICS: Here is a shortcut for finding the correlation between LBCS and NAICS in the most popular land uses:
Typical HOUSING types
-
1 | Household activities (Residential activities)
- LBCS = 1100
- NAICS = null
-
2 | Transient living (Residential activities)
- LBCS = 1200
- NAICS = null
-
3 | Institutional living (Residential activities)
- LBCS = 1300
- NAICS = null
Popular AMENITYAMENITIES types
-
4 | Hotels
- LBCS = 1300
- NAICS = 721110
-
5 | Restaurants
- LBCS = 2500
- NAICS = 720000
-
6 | Night live
- LBCS = 2540
- NAICS = 620000
-
7 | Leisure and Wellness
- LBCS = 6500
- NAICS = 722500
-
8 | Culture
- LBCS = 5000
- NAICS =710000
-
9 | Shopping Centers
- LBCS = 2100 + 2500
- NAICS = 440000 + 450000
-
10 | Banks
- LBCS = 2200
- NAICS = 450000
-
11 | Educational
- LBCS = 6100
- NAICS = 610000
PARK
- 12 | Parks
- LBCS = 7000
- NAICS = 712190
TRANSPORTATION
- 13 | Transportation hubs (Air, Water, rail, road transport and infrastructures as well as local urban and interurban transit systems, etc.)
- LBCS = 4000
- NAICS = 480000
SAFETY AND SECURITY
- 14 | Public Safety
- LBCS = 6400
- NAICS = 480000
WELLBEING
- 15 | Health Care
- LBCS = 6500
- NAICS = 620000
OFFICE
-
16 | Public Administration
- LBCS = 6200 + 6300
- NAICS = 920000
-
17 | Finance
- LBCS = 2200
- NAICS = 520000
-
18 | Scientific and Technical
- LBCS = 2400
- NAICS = 540000
INDUSTRY
- 19 | Manufacturing
- LBCS = 3000
- NAICS = 320000 + 330000
NATURE
- 20 | Nature
- LBCS = 9000
- NAICS = 712190
More advanced Types Examples
Below are some more examples of CityScope types. These can be copy and pasted or modified for use in different CityScope projects: A single grid-cell may contain multiple LBCS and multiple NAICS on different floors or even on the same floor. Therefore, the value of each attribute is formatted as a list of objects. The object in the list represents a grouping of floors starting with the lower-most floors. Each object contains the mix of uses within that floor-group. For example, the following represents the NAICS attribute for a grid cell where:
Mixed use building
- The lower 30% of floors are devoted to a mix of "541310" (architectural services) and "541330" (engineering services).
- The upper 70% of floors and is devoted to a mix of "23" (Construction), "42" (Wholesale) and "61" (Education).
{
"NAICS": [
{
"P": 0.3,
"use": [
{
"541310": 0.5,
"541330": 0.5
}
]
},
{
"P": 0.7,
"use": [
{
"23": 0.3,
"42": 0.4,
"61": 0.3
}
]
}
]
}
The number of floors is independent of the type and specified separately by the user. Therefore, if the user assigns 10 floors to this grid cell, the lower 2 floors will be a mix of 541310 and 541330 and the upper 10 floors will be a mix of 23, 42 and 61. In most cases, the type specification will not require such a detailed level of partitioning of types. If for example, the grid cell has only a single usage type, the same data format will be used but the list will only contain 1 object of length 1. For example, the following represents the NAICS attribute for a grid cell solely devoted to "54" (Professional, Scientific and Technical Services).
{
"NAICS": [
{
"P": 1,
"use": [
{
"54": 1
}
]
}
]
}
Residential Type (100% detached units)
{
"NAICS": null,
"LBCS": [
{
"P": 1,
"use": [
{
"1120": 1
}
]
}
]
}
Residential Type (detached units) with ground-level grocery store
{
"NAICS": [
{
"P": 0.1,
"use": [
{
"4451": 1
}
]
},
{
"P": 0.9,
"use": null
}
],
"LBCS": [
{
"P": 0.1,
"use": [
{
"2150": 1
}
]
},
{
"P": 0.9,
"use": [
{
"1120": 1
}
]
}
]
}